Project A03
Role of enteric nervous system homeostasis in gut-nervous system immune signaling
Project Description
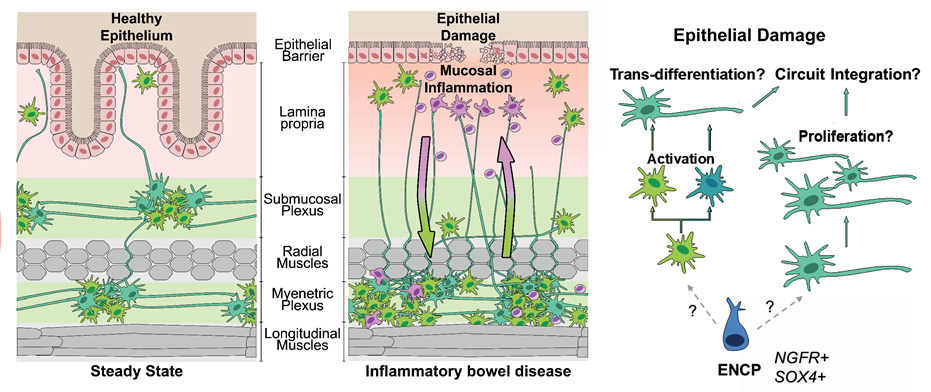
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are more frequently affected by neuropsychiatric, -degenerative and -immunological disorders. It is hypothesized that the co-morbidities of IBD with central nervous system (CNS) diseases reflect communication between the gut and the brain, but the mechanistic underpinnings of this communication remain largely unknown. The enteric nervous system (ENS) is anatomically and functionally connected to the gut and the brain and constitutes a candidate gateway for gut-brain communication. Our preliminary data demonstrate that intestinal inflammation is associated with pronounced ENS remodeling and increased innervation of the inflamed mucosa. Here we investigate the hypothesis that ENS homeostasis under steady-state and pathological conditions depends on the generation of new neurons and that disruption of ENS neurogenesis contributes to IBD and mediate pathological signals from the gut to the CNS. We will investigate this hypothesis through the in-depth histological, molecular and cell biological characterization of sophisticated transgenic mouse models in the context of different experimental IBD models. Results from this study are expected to uncover novel mechanisms on the role of the ENS in gut-brain communication.