Project A01
Deciphering immune interactions between human iPSC-derived enteric neural lineages and 3D intestinal epithelial organoids in mucosal inflammation
Project Description
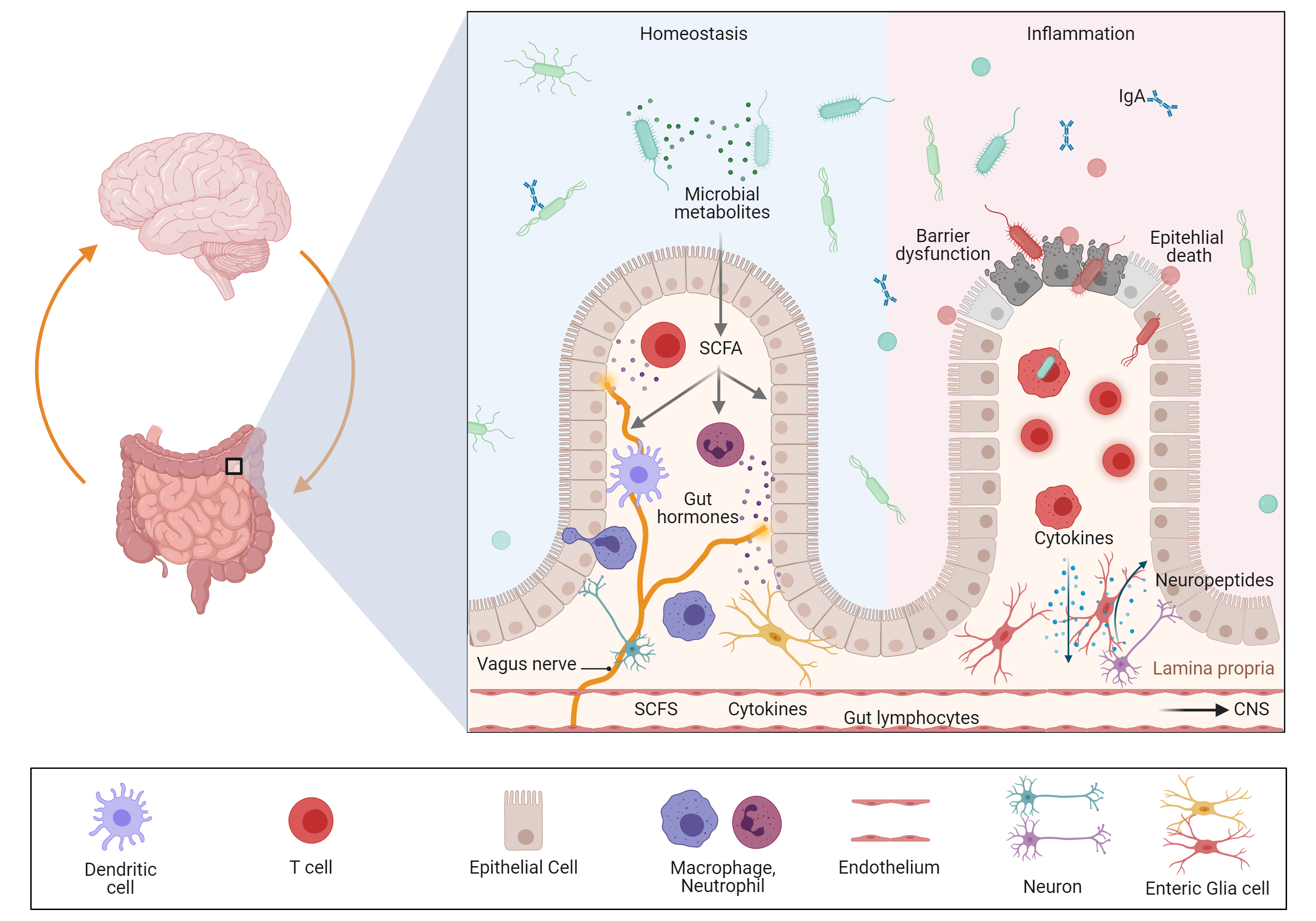
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system, linked by the enteric nervous system (ENS), among others. Consistently, inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) can be associated with neuroinflammatory changes, while neurodegenerative disorders can be linked to alterations in the intestinal environment. The ENS regulates diverse aspects of gastrointestinal homeostasis and is tightly interrelated with the intestinal epithelium. However, it is unclear how these processes are regulated in the human gut during homeostasis and intestinal inflammation. Specifically, there is a lack of preclinical models to study the interaction of the ENS with the complex environment of the human gastrointestinal (GI) system.
Here, we will study immune crosstalk between ENS and mucosal immune and epithelial cells by use of human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived enteric neural lineages (ENL) combined with primary mucosal immune and epithelial cells derived from patients with Parkinson disease (PD) and IBD. Functional validation of identified pathways will be performed using human organ culture systems and humanized mouse models in vivo. The expected results will investigate the role of the ENL as a transducer of neuroinflammation and allow new insights into the ENS-GI crosstalk. These human models can be used in an autologous manner or as humanized mouse models for prediction systems in personalized medicine and may lead to the design of novel therapeutic interventions.
Project Leaders:
Prof. Dr. med. Markus F. Neurath
Director of Medicine 1 - Gastroenterology, Pneumology, and Endocrinology
PhD students:
Master Student: